One of the major challenges facing America is how to manage natural resources, such as farmland soil, while our population is growing by millions every year. The paradox is that as America’s population grows so does the demand for housing, and food. But every year development and desertification is consuming the total acreage of farmland necessary for growing food. America’s capacity to provide basic resources (water, food, fiber) to its citizens is on a collision course with its population growth.
Related Immigration Factsheets: Farms and Food Security, Water, Biocapacity.
Almost a third of land in America is affected by desertification, the process by which fertile land becomes desert. Much of the arid and semi-arid lands of the western and southwestern United States are highly vulnerable. Overgrazing and degradation of the natural vegetation cover can contribute to erosion and desertification. In addition, excessive withdrawals of groundwater to irrigate crops and supply cities is exceeding the recharge rates of aquifers, resulting in a rapid decline in the height of the water table.
An infamous example of groundwater depletion by over-pumping is the sandstone Ogallala aquifer in the Southwest, which has contributed to desertification in Nebraska, Kansas, Oklahoma and Texas. Moreover, the salts left behind on the soil surface after the irrigation water has evaporated results in land degradation through salinization, toxic conditions for crops, and contaminated groundwater. Salinization resulting from decades of heavy irrigation has compromised the soil quality in California’s San Joaquin Valley, which produces much of the produce sold in the United States.
The World Desertification and Drought Day is a United Nations observance celebrated each year on June 17th. Its purpose is to raise awareness about desertification and drought, highlighting methods of preventing desertification and recovering from drought. This year, the theme is to spotlight the future of land stewardship — our most precious resource to ensure the stability and prosperity of our population.
Land degradation is driven by a number of factors, including urbanization, mining, farming, and ranching. These activities involve clearing trees and other vegetation, plus crops depleting nutrients in the soil. Drought also can play a significant role. All of this contributes to soil erosion and an inability for the land to retain water or regrow plants.
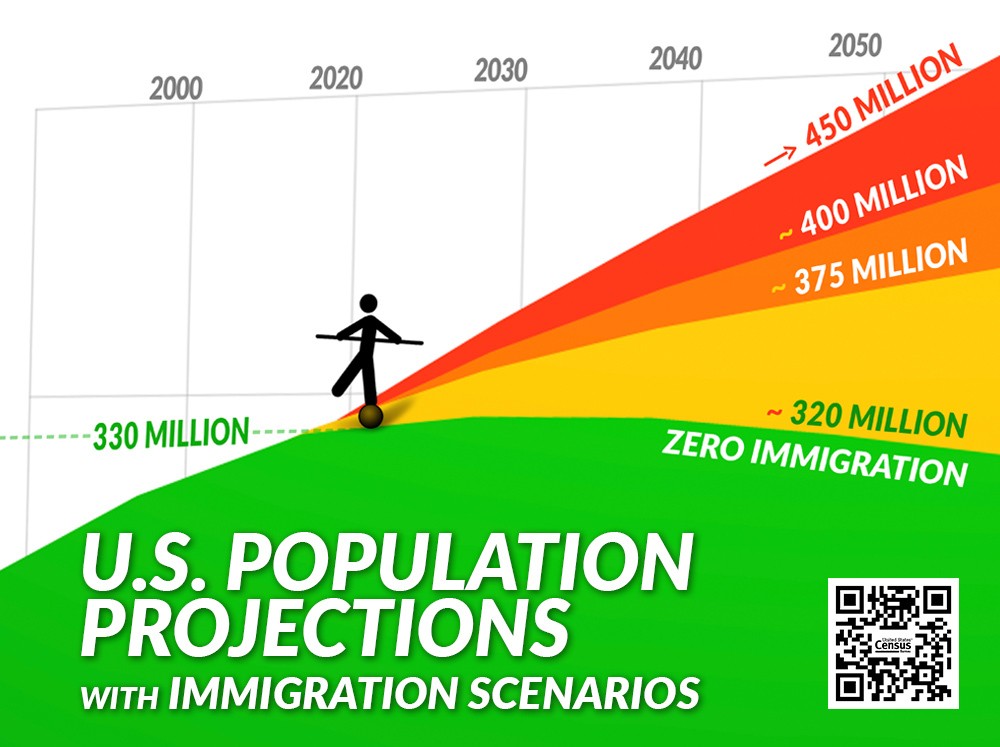
Our nation’s unsustainable growth has been primarily a result of Congress’ inability and/or unwillingness to address our immigration policies. The Census Bureau projects the U.S. population will add 50+ million people by the Year 2060, with about 90 percent of that growth resulting from immigration.